In this article, we'll cover:
If you’ve ever wondered how products go from mere materials to merchandise on the shelves, you’ve come to the right place. It’s time to talk about the logistics industry. Since the outbreak of the Pandemic in 2020, eCommerce industries have experienced skyrocketing demand.
COVID has made precision logistics more important than ever before and logistics management that bit more complicated. But with the help of automation, it is possible to execute complex logistical operations that end in reliable order fulfilment and satisfied customers.
Today the Internet of Things (IoT) and advanced Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software are streamlining challenging logistical operations with real-time data and information flows.
In this article, we’ll be discussing the ins and outs of logistical processes to glean a better understanding of what it really takes to satisfy our soaring consumer demands.

What is logistics?
In its most basic form, logistics refers to the planning and execution of a complex operation. This can include both long and short term logistics operations. Logistics management is part of the supply chain. It involves planning, implementing, and overseeing the effective storage of goods and their transportation from the point of origin until the final destination (the point of consumption).
In other words, logistics manages forward and reverse merchandise flows.
Logistics managers have to move products from their point of origin to their point of sale under optimum conditions. That means managing inventory, equipment, locations, distributors and costs. It has a knock-on effect at different levels of the economy. Good logistics has the power to minimise costs, increase profits and drive international imports and exports. Logistics is a precision process that relies on targeted planning and resource management for its success.

Main components
Logistics comprises five essential components. Logistics companies are responsible for executing each one of these components to the highest degree of accuracy. Here are the five key components of any logistician’s job.
1. Demand planning
To guarantee customer order fulfilment, demand planning is an essential logistics function. By ordering merchandise in the correct quantities and at the right price and mobilising suitable transport, customer demand is met and profits protected.
2. Storage and materials
Because demand is unpredictable, it’s important to have surplus goods on standby until consumers demand them. Warehouses are responsible for the storage, care, retrieval, packaging, and unitisation of merchandise. Warehouse management systems (WMS) optimise storage capacities, equipment (forklifts, for example), retrieval speeds, and warehousing processes.
3. Inventory management
Inventory management controls the flow of goods in and out of a warehouse. It dictates how much stock to hold and where to locate it using targeted data to predict consumer demand.
4. Transportation management
Logistics involves mobilising different modes of transport to move merchandise from one stage of the supply chain to the next. Merchandise might need to travel via road vehicles, freight trains, shipping, or even air travel for long-distance supply chains using transportation management software.
Consolidation is the process by which shipping companies or carriers combine multiple smaller shipments in one. This speeds up deliveries and keeps costs low.
5. Control
Logistics is a complex operational procedure that requires a lot of precise information to be effective. Forecasting demand, transportation times, and inventory are crucial to keeping the operations to a tight timescale.
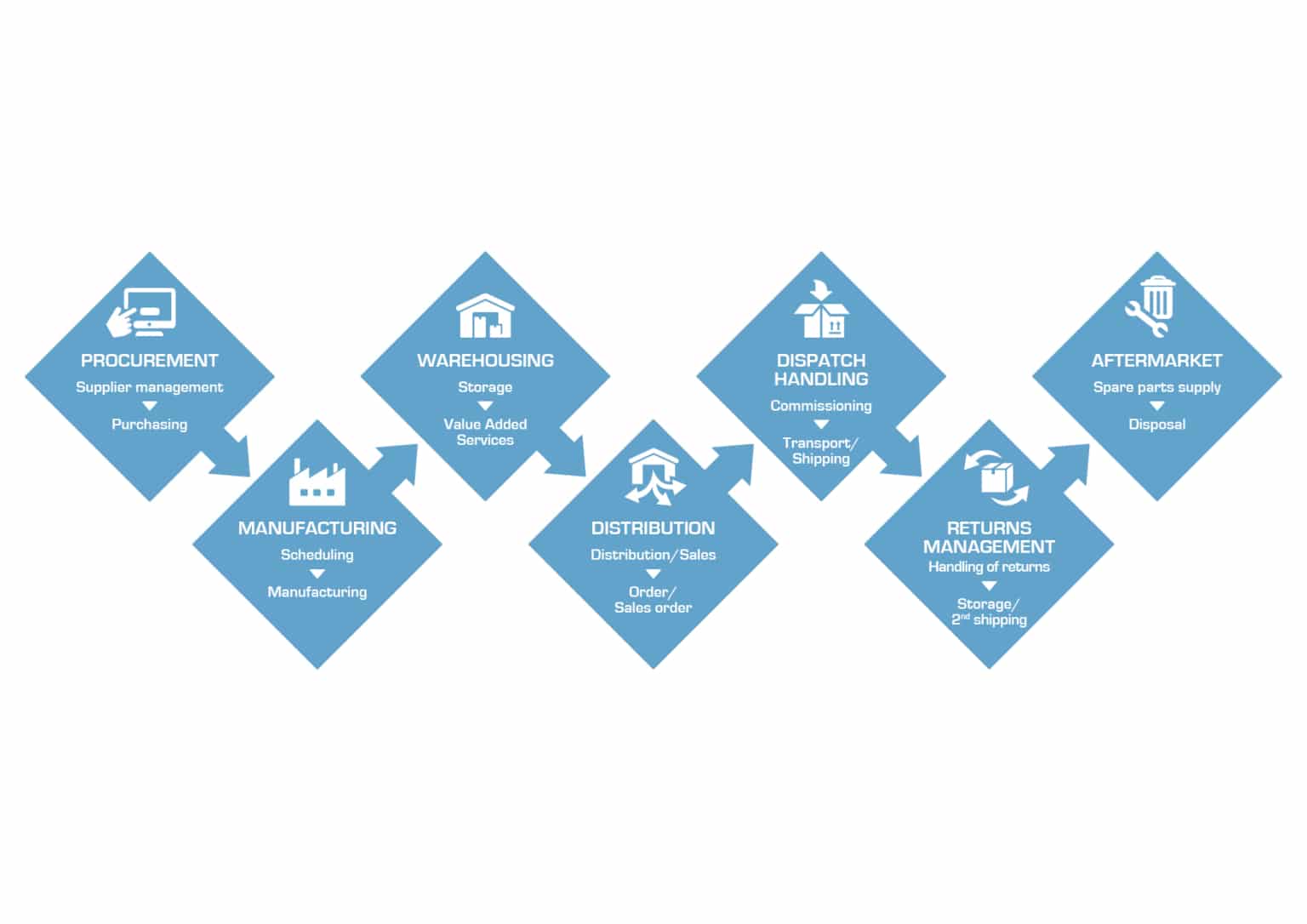
Functions of logistics
The five components of logistics help with the execution of key logistical functions. But on top of planning, storing and transporting, logistics encompasses numerous other very important operations.
These include everything from network design to order processing and procurement to sustainability targets.
Design
Management professionals design precision logistics networks covering different locations that make up the supply chain. They optimise routes between manufacturers, warehouses, transportation service providers and final retailers to ensure an efficient service.
Orders
Logistics management also involves processing customer orders. And a lot of them, at that. Orders have to be received, sorted, filed, recorded, and then fulfilled promptly. Keeping this process reliable and efficient is an essential logistical function.
Procurement
For products to reach the shelves, someone has to deal with the raw materials. Logistics management involves obtaining high-quality raw materials from external suppliers and negotiating the best price for the manufacturer.
Reverse logistics
Reverse logistics plans and executes the reuse or proper disposal of products and materials. In short, this process works backwards to ensure excess or used merchandise is dealt with sustainably. Some companies even have sustainability targets for which it is the responsibility of logisticians to execute.

Why logistics is important
It doesn’t matter how fantastic your product is if it’s not reaching your customer where and when they need it. That is why logistics is so essential for business success. Meeting customer demand is the central pillar of the supply chain and logistics’ overarching function.
But that’s not all. By digging a little deeper, we will realise that logistics is important for the everyday functioning of so many core business processes.
Efficiency
Logistics teams use real-time data to optimise supply chain efficiency. By tracking the movement of merchandise, roadblocks can be identified to prevent further disruptions.
Supply chain
Without logistics, supply chains would descend into chaos. Logistics ensures that merchandise arrives in the right place at the right time and streamlines every step along the way.
Delivery
In today’s fast-paced marketplace, delivery time expectations are becoming shorter. Logistics is essential to maintaining distribution networks and the timely and safe transportation of goods to meet customer demand.
Quality
Good logistics will put in place reliable strategies that improve customer service. That could mean speeding up delivery times or reducing costs by building relationships with supplies.
The difference between logistics and supply chain management
Logistics and supply chain management are closely related processes. But they are not entirely alike. They each make up a separate part of the commercial process.
Picture supply chain management as the broader canvas. It encompasses an extensive network of functionaries that execute the movement of merchandise from production to consumer. That means everyone from vendors to warehouses and transportation services.
Picture logistics as a process painted within the supply chain canvas. It can be carried out in house by a single company or by outsourcing to third-party logistics providers. It is concerned with optimising every process along the supply chain to lower prices, improve services, and boost profits.
The key ingredient
Logistics is a complex process, but it boils down to one thing—customer experience at the end of the day. Precision logistics have the power to be cost-effective, improve quality, and speed up delivery fulfilment. With strategic, data-led planning, logistics professionals have the capacity to drive sales and boost commercial profits.
Learn how RingCentral can help improve the customer experience for your business.
Originally published Apr 15, 2021, updated Jul 24, 2023