In this article, we'll cover:
You want your business to do well and plan on setting goals to optimise your processes. But how can you reliably compare your current performance to your past performance? KPIs (or “key performance indicators”) are a great way to evaluate how your company is doing and make actional and strategic goals to move your business forward. This method provides important analytics to improve performance and customer satisfaction.
What are key performance indicators (KPIs)?
KPIs are a measurement of how well an organisation is performing against its key objectives. This definition may seem vague, but that’s intentional – what’s important or “key” to one business may not be to another. Your key performance indicators should be critical to your business in particular.
Using KPIs can provide a focus for performance measurement. They can be qualitative or quantitative measurements that help your company with decision-making. However, do not confuse KPIs with business metrics. KPIs measure how effectively you are achieving business objectives. Metrics, on the other hand, track the status of a business process.

Attributes of KPIs
- Available and measurable: Whether qualitative or quantitative, you can’t analyse data that does not exist or is impossible to measure. Any key objective you identify needs to be based on attainable data and result in a measurable value.
- High impact. The important aspect of KPIs is the “K”. Whatever you choose for your KPIs needs to be critical to your business processes.
- Relevant. Any measurements you take should be relevant to the running of your business. Your identified objectives should align with your overall business goals.
- Easy to monitor. It would be best if you ran KPIs on a regular schedule. Using automation, you can monitor them in real-time. Otherwise, you can check in on a weekly or monthly basis. They should measure something easy to keep track of.
- Practical. KPIs should inform any decision-making processes, from management meetings to project delegation. It should be simple to see what is and is not working to achieve your goals.
What are the benefits of KPIs?
Key performance indicators highlight how well a business is doing. Managers and business owners are often overconfident in their measurements of how the company is meeting its goals. The only way to know what processes affect your bottom line is to perform data-driven analysis.
For example, Tesco PLC grocery store recognised the importance of data-driven decision making. They prioritised gaining insights from customers by developing a way to measure and track shopping habits. To find out what individuals placed in their shopping cart, they introduced Clubcard. It transformed what they think they know about their customers. The CEO, Sir Terry Leahy, said, “We don’t spend a pound or dollar on a store without talking to our customers”.
They moved from being intuitive to being analytical, which has increased their profitability and customer satisfaction. The ability to uncover the drivers behind things like customer satisfaction is just one benefit to KPIs. Here are some others.
1. Ability to measure targets
Knowledge is power. Sometimes it can be not easy to see the larger picture.
In a study by Cascade, 25% of companies said that measuring implementation of change was their toughest challenge. By using KPIs, you can actively measure the implementation of the changes you make in your company. Measuring targets is arguably the most important use of KPIs.
2. Create a learning environment
Consistently using KPIs generates an atmosphere that encourages learning. Your company does not just have superficial goals that never get met. Noticing an unfavourable KPI gives your team the chance to discuss it and use the data to pinpoint areas of improvement. You can learn from historical data and apply that knowledge accordingly.
3. Gather vital information
KPIs provide you with an immediate snapshot of your company’s overall performance. As well as improving businesses processes, they allow you to provide the most accurate data for stakeholders, letting them know how their investment is doing.
If you use automated systems to measure KPIs, you will get real-time data to make systematic adjustments. Now, your business decisions are no longer informed guesswork. Instead, they’re based on the most up-to-date information.
4. Encourage accountability
It is difficult to hide behind data. If one department isn’t performing well, KPIs should let you know what is going wrong and why. It is important to create accountability, especially in collaborative work environments. The result can make management and team members more productive.
5. Boost morale
On the other hand, KPIs can drastically boost morale. It can be encouraging for employees to know they have met their goals for the month or year. Rewarding staff for meeting KPIs is a great way to develop an environment that celebrates success. This can be through monetary incentives, team lunches, or other rewards.
Key steps in the KPI process
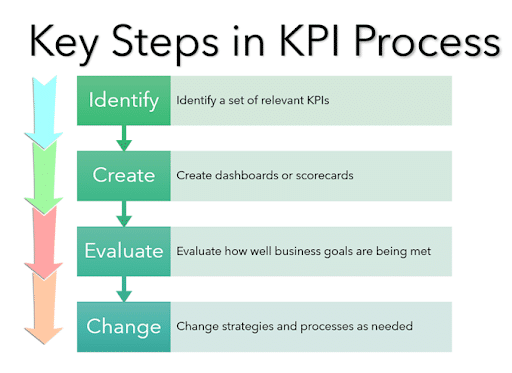
The key steps in the KPI process allow you to analyse your company’s data methodically. It allows you to implement and evaluate changes, as well as create a system of analysis. The basics are Identify, Create, Evaluate, and Change.
1. Identify
This step requires you to identify a set of relevant KPIs that your company will track. These must be structured and selected methodically and thoroughly. Everyone you choose needs to have a close and direct connection with your business’s overall objectives. The KPIs should be achievable and evaluate at least one aspect of business performance.
For example, if you want to increase your company’s profitability, look into what financial KPIs will help you reach that goal. You may identify that gross and net profit margin, inventory turnover, cost of goods sold, and day sales outstanding are the KPIs that your company needs to track.
2. Create
At this point, you need to create your KPI dashboards and/or scorecards. Dashboards track strategic goals and measure overall efficiency, while scorecards are pretty much progress reports. Scorecards are a quick way to measure KPIs and indicate how well your company is progressing towards its goals. Which one you decide to use depends on what you are looking for.
Scorecards
- More static
- Used to track KPIs
- Not updated in real-time
- Monitor goals
Dashboards
- Central hubs for multiple reports
- Easy to access
- Measure performance
- Offer an operational view
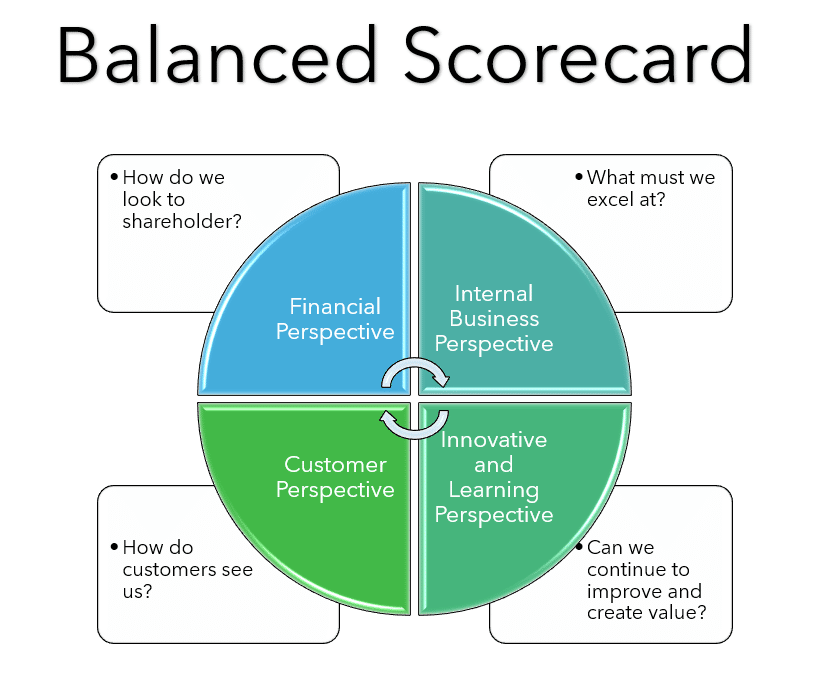
You may find that you need to use both when measuring your KPIs. You can even include scoreboards within your dashboards. If you are using a scorecard, make sure you use balanced scorecard measures. You want to look at the Internal Business Perspective, Financial Perspective, Customer Perspective, and Innovation and Learning Perspective. It allows you to evaluate every area of your business using measurements like cash flow, conversion rate, and sales.
For the financial KPIs that you identified, you can then track them through scorecards and your dashboard. The dashboard will allow you to visualise how you are progressing towards your goal. Within this dashboard, your scorecard can give you progress reports. The monitoring process should be done regularly.
3. Evaluate
The next step is to evaluate how well your business goals are being met. This is the time to consider whether you have set a reasonable goal and identified the right KPIs related to customer churn. You may use data like new customers, the number of customers, and the amount of inactive and deleted accounts.
Once you have the data, you need to evaluate your financial KPIs. Ensure you have set reasonable goals for your cost of goods sold and gross and net profit margin. Also, make sure that you consider any other KPIs that may lead to increased profitability. Look at other KPIs like Marketing and Sales. For example, customer churn may have more influence on your profitability than you first thought.
4. Change
This is when you should change processes and strategies as needed. This is not a one-off step – as you consistently evaluate, so too should you consistently make any needed changes. This keeps your company’s decision-making and processes dynamic.
Different types of KPIs
Different business objectives will require different types of KPIs to best measure performance. Each serves a different purpose and is not mutually exclusive. You may find yourself using several different types within your KPI dashboard. They include:
- Real-time KPIs
Many service-level KPIs provide an immediate view of business processes. For instance, an eCommerce site that monitors analytics in real-time can see things like abandoned cart rates, page views, and bounce rate.
- Historical KPIs
This type of KPI helps forecast accuracy by providing historical data. This helps your company plan for the future. The ability to forecast will help your company perform better on every level. For instance, if you’re a retail business, you could use this type of KPI to optimise your supply chain.
- Customer KPIs
This type of KPI deals with customer satisfaction. You can measure these by using things like the Net Promoter Score or Customer Lifetime Value. A lot of KPIs in this area will you qualitative measurements rather than quantitative ones.
- High Level and Low-Level KPIs
There are also high and low-level KPIs you should use. The first is the Business KPI (high level) which measures the performance of a core business goal. Then there are two low-level KPIs: External and Internal. External measures an external goal at the department or team level. Internal KPIs measure individual progress.
How to measure KPIs

Once you have identified your KPIs, communicate them to your employees. If you have automated business analytic software, then it will collect the data for you. But what framework can you use to gather this data?
First, you need to know what goal you are working toward. This needs to be an actionable objective. Then it would help if you prioritised your KPIs. Develop primary and secondary KPIs depending on what your business needs. Your business cannot improve everything at once, so what do you want to focus on?
After you determine your KPIs, determine your diagnostic metrics. This helps you analyse a problem and understand the cause. From there, you can determine your targets and benchmarks. Where do you want your company to be?
In summary, you should:
- Determine the Goal
- Determine Primary KPIs
- Determine Secondary KPIs
- Determine Diagnostic Metrics
- Determine KPIs Targets
- Identify Benchmarks
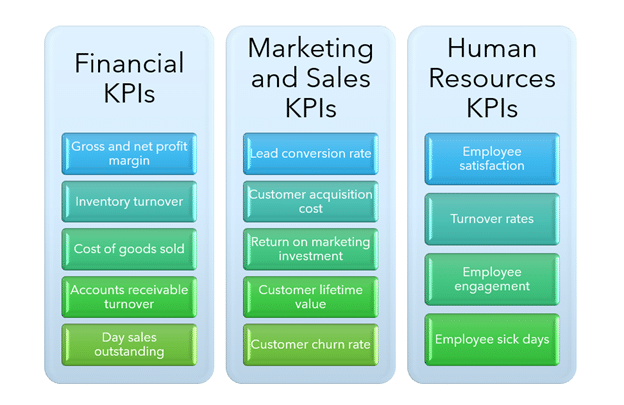
Examples of key performance indicators
There are countless KPIs you can use to measure your business performance. The department, goal, the process can determine these or even be industry-specific. Below are some examples of KPIs.
How to write and develop KPIs
Here is a quick and easy template you can use to write and develop KPIs catered to your company.
Step 1: Establish a mission and vision
Step 2: Define your core goals
Step 3: Use the SMARTER method to choose your KPIs. These are Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Relevant, Timely, Evaluated, and Readjusted.
Your KPIs need to be specific, so do not choose KPIs that are so broad they don’t give you usable data. They should also be measurable. Data that isn’t measurable isn’t useful to you. It should also be attainable and relevant. The data should be available to you and related to your company’s processes. It should also be timely, evaluated, and readjusted. Timing is everything, and you need up-to-date information. This information should then be evaluated and readjusted as necessary.
Step 4: Set up KPIs
Step 5: Determine a clear target
Step 6: Declare your strategy
Step 7: Share your objectives with your team
Conclusion
KPIs are a vital component for a successful business. They take the guesswork out of operational decisions and can help you identify areas of improvement. The best thing about KPIs is that you tailor them to the needs of your company. You and your team set the goals and can make your company a place where people want to be a part of reaching those goals.
Originally published May 10, 2021, updated Dec 13, 2023

