In this article, we'll cover:
Cross-selling is suggesting additional items to a customer committed to purchasing to increase the value of the sale. It’s an excellent growth strategy to boost revenue and customer retention. If done right, you can nurture and maximise your customer relationships and enjoy increased profits.
What is Cross-Selling?
Cross-selling is a sales tactic to generate more sales. To cross-sell is to sell a complementary product to a customer to increase the value of a previous purchase. It’s an effective marketing tool to engage an existing customer further. Cross-selling works remarkably well on eCommerce websites to enhance the customer journey and increase average order value (AOV).
Cross-selling is meant to increase revenue by persuading a new customer or an existing one to buy an ancillary product and their initial purchase. It is a selling technique meant to increase the average order value at the checkout by pairing items frequently bought together and convincing the customer that one cannot do without the other.

How Does Cross-Selling Work?
Cross-selling intends to increase revenue by taking advantage of an established relationship with a customer and identifying a complementary need not fulfilled by the original item. It is used often by online retailers, financial services firms, and even fast-food restaurants to pitch in a complimentary item right at checkout. Effective cross-selling can work wonders and translate into significant profits, as it is the easiest sales to make.
In a brick and mortar store, sales teams are trained to show additional products or services to customers standing at the checkout or on the way to the checkout. In eCommerce, cross-selling has to be built by web design into the site so that related products show up on product pages. However, it could still be as simple as recommending a conditioner when buying shampoo.
While you want to increase the number of items in the customer’s shopping cart at checkout to cross-sell successfully, it’s a good rule of thumb to pitch products that cost 10 per cent to 50 per cent of the original purchaser’s cost. Price is always a major factor.
Whether cross-selling is implemented on the product page or during the checkout process, it can be a successful sales tactic for showcasing the breadth of your catalogue and even for generating repeat purchases. Cross-selling is subtle, but alerting customers to products they did not know you offered is an excellent way to earn their trust and increase customer retention.
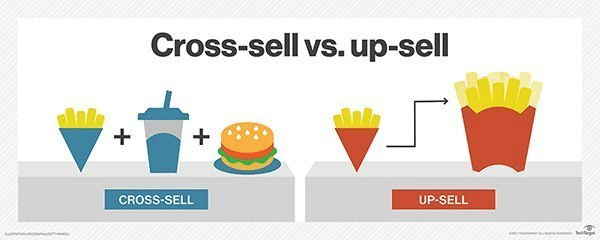
Cross-Selling vs Upselling
Upselling and cross-selling are two distinct terms that are often confused with one another. Cross-selling invites a customer to buy a complementary product that is often of lower value than the original purchase. Upselling is a sales technique to encourage customers to buy an upgraded or premium product compared to the original one.
They can be effective in tandem and do not have to be mutually exclusive. A popular cross-selling technique is being asked for fries to go with your burger at a fast-food checkout. Upselling would be to buy the combo meal or to upsize your original purchase. When done right, both techniques can be used together to provide maximum value to customers and increase revenue by not limiting customers to already-encountered products.
Why is Cross-Selling Important?
Cross-selling increases your sales and conversion rates without any additional burden on your resources. Compared with other marketing channels, recommending an add-on at the time of purchase costs next to nothing. But the corresponding increase in revenue can be substantial.
Some of your higher value products may have low margins, so pitching in an additional product with higher margins can help your bottom line. Amazon reports that cross-selling generates as much as 35% of its profits.
Cross-selling improves the overall shopping experience and helps customers discover products they might need. It is all about enriching the customer experience and not just your profit margins. Cross-selling is about identifying customer pain points and suggesting solutions. Expect customer loyalty to increase as they discover all they need under one roof.

Examples of Cross-Selling Strategies
Cross-selling has been used successfully in many industries, and there are many case studies to prove its success. Let’s look at some popular ways cross-selling has been adapted:
- The financial services industry is rife with examples of cross-selling, especially since bigger financial organisations are now offering investments, credit cards, insurance, stocks and bonds. If a customer has come in for a retirement plan, salespeople will offer different types of smaller investments as well, like life insurance or other investment products to diversify their portfolio. Cross-selling can make for an effective financial planning strategy.
- The most popular example of eCommerce cross-selling is Amazon’s “Frequently bought together” and “Customers who bought this item also bought” suggestions. Amazon has been successful with this technique because timing is key. They only promote the right products at the right time without annoying the customer with irrelevant offers and bundles.
- Many web agencies offer smaller services in addition to their main offerings. For example, if you sell SEO software, you could provide link-building services.
- Shopify has many apps that can help execute cross-selling for people who have a Shopify store. The apps help cross-sell related products as recommended products pop up when customers click add to cart. The suggestions are personalised and include add-ons and products bought together by other customers.
- “Shop the look” – A clothing retailer displays a complete outfit, so the shopper sees how it looks all together and buys more than just one piece.

How to Create an Effective Cross-Selling Strategy
For cross-selling to be an effective sales and marketing tool, there is a method to follow to increase the chances of success. Here are a few key strategies to implement before you get started:
1. Bundle offers
You can create bundle offers for items that naturally go together or without which the original purchase wouldn’t function well, like ink for a printer. The idea is to create an offer, so the customer does not get irritated by making another purchase for ancillary products. Some complementary products are not necessary but can increase the usefulness of the initial purchase, like a sound system for a new TV.
The goal is to maximise profits by bundling items that naturally go together and making sure they can successfully use their purchase. To entice customers more, a bundle is cheaper than the products sold separately. Bundling is a successful marketing strategy because it seems like a better value when multiple products are sold as one.
2. Use visuals
The human mind processes visuals faster than text. Use high-quality pictures to showcase your products. This is particularly important for eCommerce websites for fashion and lifestyle products. Customers are driven by visual cues and use videos and visual aids to show how a product looks or functions to convince customers to buy the whole package.
This tactic is used for furniture pieces where a whole room is designed, and the website gives you the option to “Shop the interior”. Visuals can be the most effective way to invite customers to add additional products to their carts by convincing them how the item can benefit them.
3. Create value
When you try to pitch in an ancillary product, you could have a small customer testimonial displayed at that point to show that another customer bought this item as well and was satisfied with their purchase.
Testimonials are the best form of social proof. This shows the buyer that the additional product is worthwhile. You could use phrases like “customers also bought” or “popular related products” to demonstrate the product’s value you are trying to cross-sell.
4. Focus on the customer experience
Cross-selling is intended to improve the customer experience. At which point you pitch in the product, and the product’s value are key factors in deciding the success of your cross-selling technique. You do not want to rub a customer the wrong way and have them abandon their cart.
Try to give them options that they feel they cannot do without and provide value for money. Map out the customer journey, so you know what touchpoints are best for repeat interactions. You could try an email follow up as part of your customer service strategy to enquire about the initial purchase and then cross-sell an item.

Cross-selling is valuable to you and your customer. Instead of spending valuable resources looking for new customers, leverage the ones you already have and try to sell them a bit more. Cross-selling is the best way to capitalise on existing customers and increase customer engagement while boosting your profits.
The customer experience is dependent on the value you add to the customer’s purchase, and it should be the most significant part of your cross-selling campaign.
RingCentral offers a one-stop-shop for an improved customer experience for your retail business. A single communication platform that connects online, in-store, and the moments in between. It helps you manage your customers on multiple channels across various touchpoints and gives them the support they need.
Visit RingCentral to request a demo for a reimagined shopping experience for your valuable customers.
Originally published Aug 16, 2021, updated Apr 10, 2023

