In this article, we'll cover:
- What Is IaaS? Infrastructure as a Service
- On-premise Infrastructure VS Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) Diagram
- How IaaS Works
- What are the Types of Cloud Computing?
- What are the differences between IaaS vs. PaaS vs. SaaS?
- What are the benefits of IaaS in Business?
- IaaS Applications
- Top IaaS Providers
- How does RingCentral support IaaS?
- IaaS moving forward
More and more businesses are switching to cloud IaaS for its flexibility and cost-effectiveness. IaaS platforms offer modern businesses the opportunity to do away with in-house IT infrastructure. They deliver on-demand computing resources to businesses over the internet.
But what exactly is infrastructure as a service?
What Is IaaS? Infrastructure as a Service
IaaS or Infrastructure as a Service is a type of online computing infrastructure. It makes up one of four cloud computing models.
- IaaS: infrastructure as a service
- SaaS: software as a service
- PaaS: platform as a service
- IaaS: internet as a service
Together, these cloud computing services cover the majority of an organisation’s IT needs. IaaS is particularly useful because it delivers computing resources to organisations over the internet, and can be scaled (and financed) according to demand.
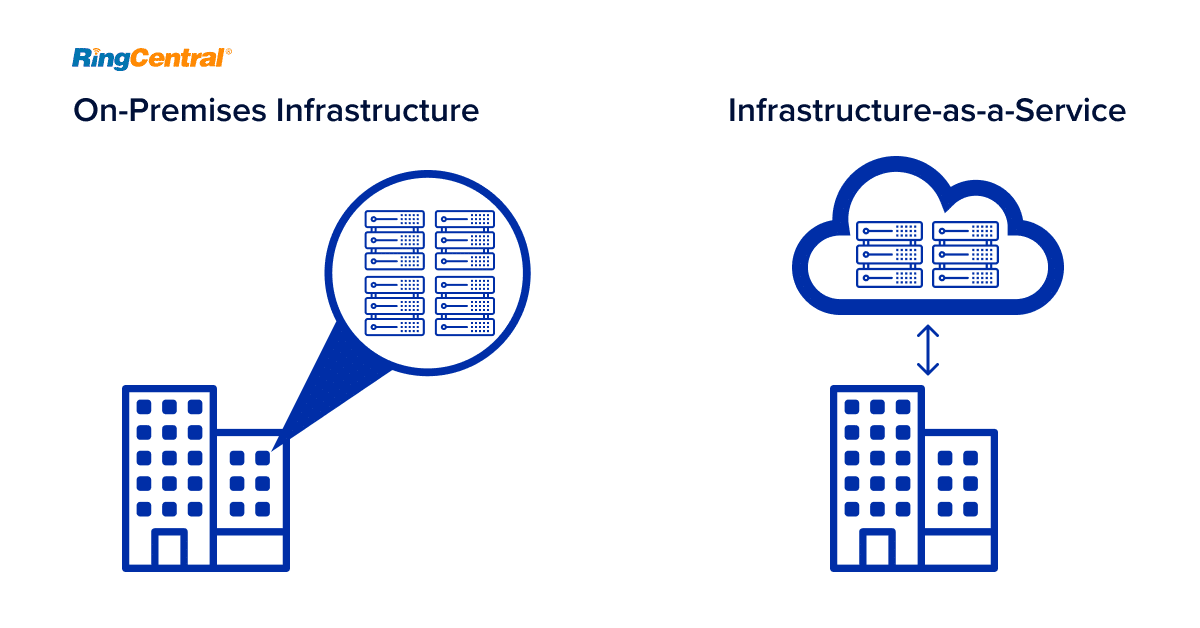
Before the evolution of IaaS cloud computing software, most businesses had no option but to host their own IT infrastructure services. This was often costly and wasteful.
In contrast, IaaS bypasses the expenses that come with physical servers. Businesses pay their cloud provider only for the services that they need, and not for what they don’t. Unsurprisingly, this has led to a huge growth of IaaS solutions.
On-premise Infrastructure VS Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) Diagram
How IaaS Works
IaaS works by mobilising a third-party cloud service provider. This cloud provider hosts the IT infrastructure. That means servers, cloud storage, hardware and virtualisation. IaaS delivery is automated. System maintenance and data storage is often handed over to the IaaS provider.
In other words, the service provider hosts the infrastructure on their client’s behalf across different datacenters making up the cloud. The client accesses the infrastructure online and uses it for the same purposes that an in-house IT infrastructure would traditionally serve. It can be accessed through computers, mobile devices, or virtual machines.
IaaS is well suited for:
- Developmental testing
- Website hosting
- Data storage and analysis
- Online applications
- High-performance computing
What are the Types of Cloud Computing?
We briefly mentioned four types of cloud offerings. Let’s delve into them in a bit more detail.
IaaS
An IaaS platform is a cloud-hosted IT infrastructure made up of virtual servers. IaaS offers virtual access to IT resources. Features of IaaS include cloud security, and a data centre for storage, backup and analysis.
PaaS
One step up from IaaS. PaaS (Platform as a Service) is a cloud-computing platform for the development and building of applications. PaaS services usually include developmental tools, middleware, operating systems, databases, and infrastructure. RingCentral’s cloud phone system is an example of PaaS.
SaaS
SaaS stands for Software as a Service and provides full applications managed in the cloud. It provides access to applications over the internet. Users no longer have to purchase and install their business applications locally, and can go completely serverless if they desire.
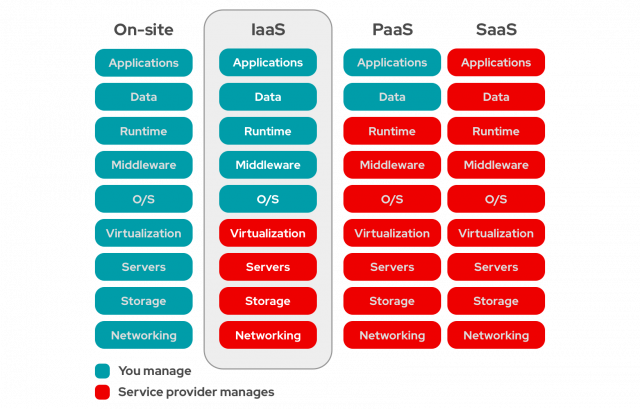
What are the differences between IaaS vs. PaaS vs. SaaS?
These three types of cloud computing can be easily confused. All three service models run on the cloud. However, they each have the distinct features that differentiate them from one another.
IaaS is a cloud-based solution for virtual IT resources. PaaS, in contrast, provides platforms from which clients can develop and deploy their business applications. Different still, SaaS is a software distribution model hosting applications for clients to make use of over the internet.
What are IaaS Pros and Cons?
The advantages of an IaaS model include:
- Lower costs. IaaS reduces capital expense by getting rid of onsite infrastructure. It’s incredibly cost-effective on an ongoing basis as businesses only need to pay for what they’re currently using.
- Rapid innovation. It guarantees up-to-date computing infrastructure ready for the launch of any new product or service. This also means that businesses can be adaptable and scale resources up or down as necessary.
- Reduces in-house operations. There’s no need to hire staff to manage in-house IT infrastructure. Instead, everyone can focus on the core business.
- Security and stability. A good service provider will offer application and data security, as well as strong disaster recovery strategies. There’s also no need to upgrade software or equipment. This should be part of the agreement with the service provider.
The disadvantages of IaaS include:
- Cyber threats. Data protection relies on the security of your service provider‘s cloud infrastructure and employees. Implementing your own measures, like firewalls, may interfere with the web applications you’re using.
- Outsourcing. Businesses will have to give up some control over their IT functions to a third-party provider, potentially making management more challenging.
- Unexpected costs. Sometimes IaaS is billed according to the precise usage of a service. This usually leads to reductions, but it can occasionally lead to unexpected increases.
- Service performance. The resilience of an IaaS service is dependent on the provider, rather than the end-users.
What are PaaS Pros and Cons?
The main advantage of PaaS is that it simplifies workload deployment. The service provider hosts and manages the underlying infrastructure, operating systems, runtimes, and middleware for cloud users. However, in addition to the disadvantages of IaaS, PaaS also restricts business flexibility and inhibits personalisation.
What are SaaS Pros and Cons?
The main advantage of SaaS is that, as well as the entire IT infrastructure, the service provider also hosts all user applications. In other words, a SaaS user does not have to install anything. Everything runs on the provider’s infrastructure. However, this level of outsourcing, again, can be inhibiting and requires users to give up control over operations.

What are the benefits of IaaS in Business?
IaaS can be extremely useful in a business context. The cloud service offers flexibility, scalability, and speed on a level unimaginable under traditional IT infrastructures. It is far easier to expand a business that has an IaaS foundation.
Maintain a Growth Mindset
Businesses can scale up or down depending on demand at a particular time. This saves money and reduces the impact of wasted or insufficient resources. Load balancing enables you to control traffic distribution, ensuring high availability.
Save Costs
Maintenance costs drop when businesses switch to IaaS. Businesses no longer rely on an on-premises data centre or hardware, reducing wasted spending and expensive bills when things go wrong.
Have the Flexibility You Need
IaaS outsources a chunk of labor from a business’s internal teams, freeing up time and money previously spent hiring specialist staff. The amount of outsourcing depends on how much of your infrastructure uses public cloud providers, and how much uses a private cloud.
Get Set Up Faster
Businesses that use IaaS can deploy and update applications at speed. That’s because the cloud provider can offer just the right amount of infrastructure when and where a business requires it.
Have a Backup Plan
IaaS allows businesses to access their IT infrastructure virtually from any location. This also means that the service provider can offer greater availability. Facilities are distributed across multiple facilities helping to avoid single-points of failure.
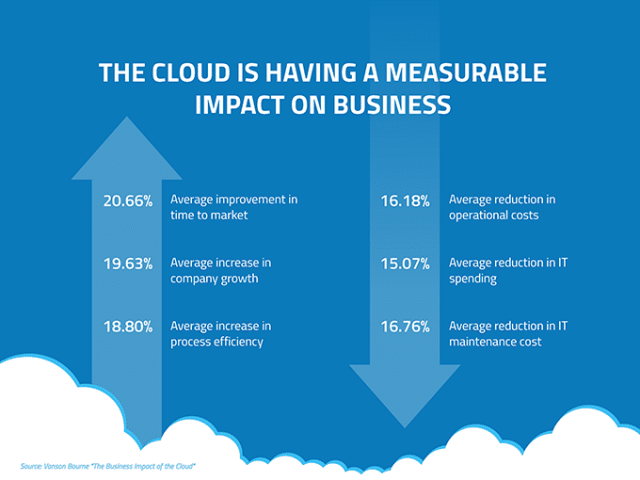
IaaS Applications
IaaS is useful in many ways. The cloud service can be applied across a broad range of business functions. Some of the main ways IaaS can help businesses include:
Test and development
IaaS lets teams set up and dismantle test and development environments quickly and economically. If you use automation in your testing, you can easily set it up, leave it running and bring new applications to market at speed.
Website hosting
Websites that run on IaaS are often less expensive than their traditional web-hosted equivalents.
Storage, backup, and recovery
Using IaaS saves money spent on specialised storage management and supports unpredictable storage demands. It also helps with regular back-ups, improved disaster recovery, and can avoid data loss.
Web apps
IaaS is extremely useful for fast application development. It facilitates flexible prototyping, experiments, and fast-paced infrastructure updates. These web applications can be built using an API or a custom dashboard.
High-performance computing
IaaS is sometimes applied to batch computing, substituting high-performance or grid computing systems. IaaS can be applied for rendering, encoding, genetic sequencing, modeling, and analytics purposes.
Big data analysis
IaaS is increasingly chosen over on-premises data centre infrastructures. You can use IaaS in place of an internal virtualisation environment to host critical applications.
Top IaaS Providers
Let’s take a closer look at some of today’s leading IaaS providers. Before choosing a cloud provider, it’s important to look into the services offered by each and choose a package that best suits your business needs. Make sure to read up on service level agreements (SLAs) to see exactly what they provide.
- Amazon Web Services (AWS): Top features include Simple Storage Services (S3), Glacier and compute services like the Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2).
- Google Cloud Platform: Offers storage and computing services via the Google Compute Engine.
- Microsoft Azure: Also offers storage and computing services via the Google Compute Engine.
- IBM Cloud: offers next-generation hybrid cloud platforms, with advanced data and AI capabilities.
- Alibaba Cloud: offers integrated cloud products and services for scalable, secure digitisation.
- Oracle Cloud: offers on-premises, high-performance computing running cloud-native.
- Virtustream: offers enterprise-class cloud services for complex IT landscapes.
- CenturyLink: offers communications, network services, cloud, and managed service solutions.
- Rackspace: offers proven multicloud solutions across apps, data, and security.

How does RingCentral support IaaS?
As more and more businesses move their applications to the cloud, many have started to revisit and improve their wide area networks (WAN). Businesses are finished with landlines and want flexible communications to match their IT Infrastructures.
RingCentral supports IaaS by providing business phone systems optimised for IaaS functionality. There’s a range of options within existing network architectures that help organisations, from business to academia, deploy cloud communications and contact centre solutions more effectively.
IaaS moving forward
All in all, IaaS offers flexibility, security, business continuity, and savings. By outsourcing IT infrastructure to a cloud service provider, businesses can focus their workforce and save money, and secure data storage, backup, and analysis.
These automated systems have the potential to take advantage of the Internet of Things (IoT) and store vast amounts of data. RingCentral’s telecommunications options support cloud computing with phone systems optimised for full IaaS functionality.
Originally published Dec 04, 2020, updated May 15, 2021